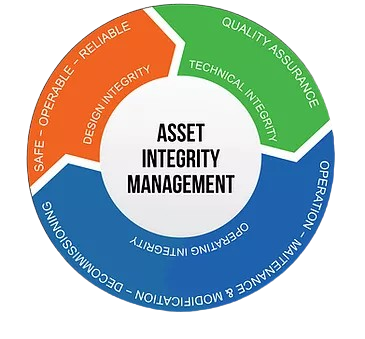
Asset Integrity Management System (AIMS) refer to comprehensive frameworks and processes implemented to ensure the continuous and reliable, efficient and effective performance of assets throughout their lifecycle. AIMS involves strategies, procedures, and technologies aimed at maintaining asset integrity, minimizing risks, optimizing maintenance and inspection practices, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
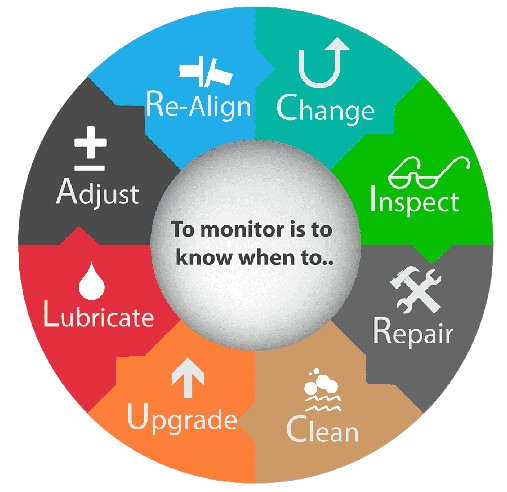
Inspection Engineering focuses on planning, executing, and managing inspection activities for assets. Inspection engineering involves developing strategies -for inspecting assets such as equipment, pipelines, structures, and facilities to assess their condition, detect potential defects or failures, and ensure compliance with safety and regulatory standards. This discipline utilizes various inspection techniques, tools, and technologies to gather data, analyze asset health, and make informed decisions regarding maintenance, repair, or replacement actions. Inspection engineering plays a crucial role in AIMS by contributing to the overall asset integrity, reliability, and safety of the organization's operations.
Benchmark Consulting Engineering L.L.C provide specialized services for Asset Integrity Management and Inspection Engineering that involve conducting the following: